June 25, 2021
By Darren Hulem, Senior IT and Risk Analyst

An exponential increase in the number of ransomware attacks in 2021 has many businesses and nonprofits wondering whether they are next. In recent months, well-known ransomware victims made headlines when they elected to pay the ransom to quickly recover data and return to normal operations. Is your organization prepared to make a similar decision, and equipped to restore critical data from backups? An incident response plan with disaster recovery procedures offers organizations the best chance for surviving a ransomware attack and minimizing damage to the organization.
Developing an Incident Response Plan
The incident response plan and accompanying disaster recovery plan clearly outline the procedures to be followed after ransomware has been detected within the organization’s IT resources. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) an incident response plan should include four sections.
Preparation
Ensure everyone at the organization understands his or her role in the event of an incident. Develop scenarios to ensure that the plan works as intended.
Detection & Analysis
Determine if an incident occurred, the type of incident involved and its severity.
Containment, Eradication & Recovery
Stop what is causing the incident before any further damage is done and restore affected systems.
Post-Incident Activity
Conduct a lessons learned exercise identifying whether documented procedures were followed and if they were adequate. This also includes steps to potentially avoid this scenario in the future.
For more information on these recommendations, review NIST’s Computer Security Incident Handling Guide.
The 3-2-1 Rule
The 3-2-1 Rule for backups is a recommended best practice for organizations who want to protect their critical data assets. It stipulates that the organization should always have 3 copies of its data, store those copies on two different media types and keep one backup copy offsite.
The offsite backup is important, but organizations should confirm that any backups are inaccessible by the same machines they are backing up and cannot be changed with backup immutability. (Immutability is a time window you can set on backup data. Data cannot be modified and/or deleted until that time period is over.)
Backup Retention Policy
Depending on the organization’s backup retention policy, backups may be completed once an hour or once a day. Offsite backups may be limited to just once a week or even monthly. Establishing a backup retention policy as part of the disaster recovery plan is essential to responding to a ransomware attack and making important decisions leading to the recovery of data.
Important acronyms: MAD, RPO and RTO
During plan development, an organization should determine their maximum allowable downtime (MAD), Recover Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO).
MAD = How long can a service or system be down before the organization cannot continue normal operations?
RPO = The maximum amount of acceptable time that data can be lost following an incident.
RTO = How long it takes to restore from an incident.
There is an inverse relationship between restoration time and the cost of any backup solution. Understanding your current RTO will help your organization strike the right balance between possible downtime in the case of an incident and the ongoing cost of a backup solution.
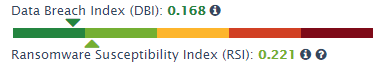
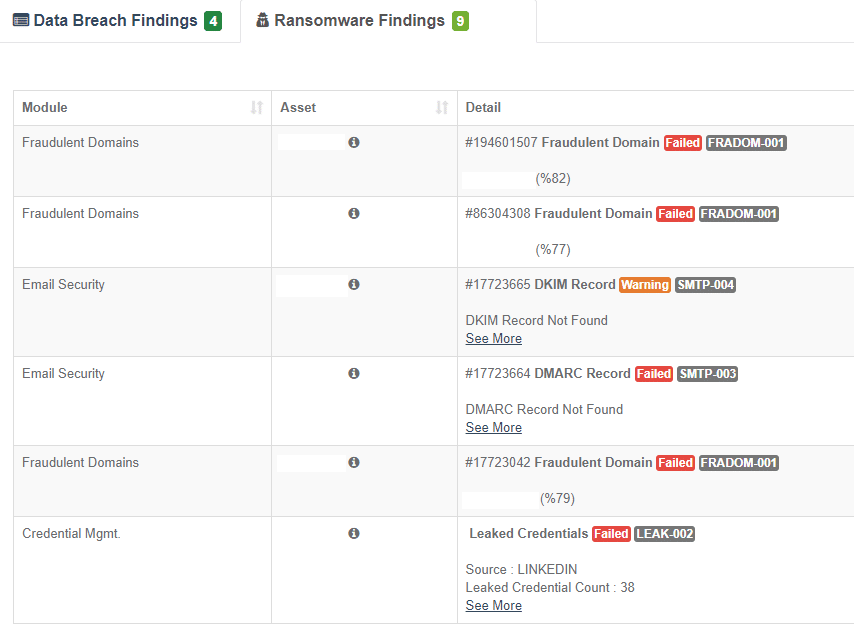
Ransomware Susceptibility Index
How vulnerable is your organization to a cybersecurity incident, including a dreaded ransomware attack? GRF’s Cyber Threat Assessment Scorecard now includes a ransomware sustainability index to help organizations assess their risk level, identify top areas of risk, and select appropriate best practices to remediate these risks from an external perspective.
Watch a demo of the scorecard and contact Darren Hulem, Senior IT and Risk Analyst for more information and pricing. For more information on building organizational resilience, download our business continuity planning whitepaper.