December 5, 2018
American educational reformer Horace Mann called education “the great equalizer.”1 In football, it’s been said that turnovers are the great equalizer. And anyone who’s ever watched CBS’s “The Amazing Race,” knows airport delays are the equalizer in a race around the world.
In taxes, there’s also an equalizer of sorts. It’s called the alternative minimum tax (AMT). Instituted in 1969, it was intended to ensure that the very rich didn’t pay a lower effective tax rate than everyone else.2
In recent years, however, the “very rich” aren’t the only ones who need to be concerned about the AMT. More and more middle-class Americans are being forced to pay it. Today about 5 million tax filers pay about $35 billion in additional tax.3
What Is The AMT, Exactly?
It may be easiest to think of the AMT as a separate tax system with a unique set of rules for deductions, which are more restrictive than those in the traditional tax system.
The only way to know for sure if you qualify for the AMT is to fill out Form 6251 from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). It may be worth doing just to be sure, especially if you are a high income earner who can claim sizable tax breaks. Of course, under the 2017 tax law, many traditional tax breaks are limited, including personal exemptions and the state and local tax deduction.
If you should have paid the AMT and the IRS discovers that you didn’t, you may owe back taxes and could also have to pay interest and or penalties.
The AMT Language
Because the AMT system has complicated rules and provisions, it’s a good idea to consider consulting legal or tax professionals for specific information regarding your individual situation. And remember, the information in this material is not intended as tax or legal advice. It may not be used for the purpose of avoiding any federal tax penalties.
If you want to avoid any potential surprises at tax time, it may make sense to know where you stand when it comes to the AMT. The time and energy you spend today may be worth the investment.
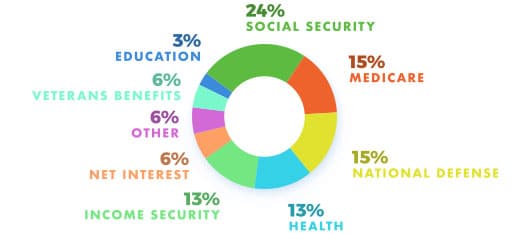
Where Does All that Money Go?
Here’s a breakdown of how the federal government spends its revenues.
1 Brainyquote.com
2 Congress enacted the first Alternative Minimum Tax in 1969.
The law was repealed and replaced by the Tax Equity and Fiscal Responsibility Act of 1982.
3 CNNMoney.com, January 2018
The content is developed from sources believed to be providing accurate information. The information in this material is not intended as tax or legal advice. It may not be used for the purpose of avoiding any federal tax penalties. Please consult legal or tax professionals for specific information regarding your individual situation. This material was developed and produced by FMG Suite to provide information on a topic that may be of interest. The opinions expressed and material provided are for general information, and should not be considered a solicitation for the purchase or sale of any security. Copyright 2018 FMG Suite.
© 2018