September 12, 2022
Limited budgets traditionally prevented organizations from conducting comprehensive Internal Audits.
Developing a process for continuous improvement and risk management is a large undertaking, however, it is important for the long-term sustainability and growth of your organization. Thanks to the advancement of auditing technologies, it is possible for organizations of all sizes to structure affordable, tailored Internal Audit plans that mitigate high-risk areas.
Using emerging technologies for risk management and audit procedures can be done cost-effectively today using creative strategies, such as co-sourcing or outsourcing with subject-matter-experts and/or bringing these technologies in-house.
GRF has worked with many organizations to create robust internal audit programs that still fit within limited budgets, and we offer two examples of how this can be done. The first step for any internal audit is to perform a risk assessment and identify the necessary skills, knowledge and expertise required to properly administer the audit procedures and manage the technology.
STEP 1: Identify Risk and Risk Response
Your organization should have a formally documented and implemented process for performing periodic comprehensive risk assessments (if you don’t, take a look at our Enterprise Risk Management Guide for Nonprofits or Best Practices in Enterprise Risk Management white papers). The results of this assessment are to quantify the risks to the organization’s strategic objectives and prioritize the risk response plans.
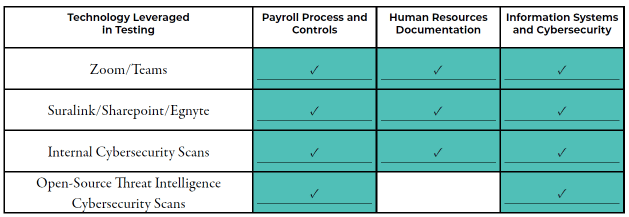
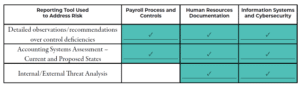
GRF has worked with various companies to help them mitigate identified risks. In one example, an organization we’ll call “Company A” is a $200M nonprofit organization. This company conducted an assessment and identified key risk areas in Payroll Process and Controls, HR Documentation, and Information Systems and Cybersecurity.
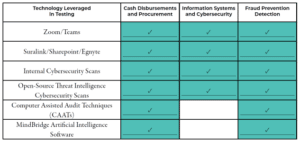
Company B is a $20M government contracting organization that decided to perform Internal Audits within Cash Disbursements and Procurement, Information Systems and Cybersecurity, and Fraud Prevention/Detection. Both organizations had a similar budget to perform the Internal Audit procedures and reached out to third parties to leverage subject-matter-experts on the various topics.
STEP 2: Identify and Incorporate Technology Into the Audit Process
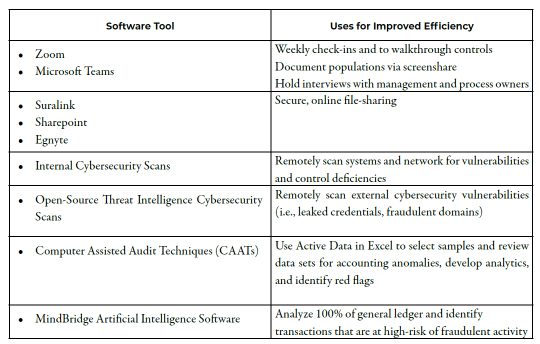
Performance of detailed audit procedures can be complex and time-consuming, which historically made outsourcing these services expensive. Technologies today support complex, high-value procedures that can be performed remotely, rapidly, and affordably. In order to perform the most efficient/effective audit procedures that address the identified risks, meet engagement objectives, and fit within both clients’ budget constraints, GRF developed our audit plans to utilize the following technologies:
Due to the complexity of the processes for Company A, GRF leveraged online communication platforms to perform detailed walkthroughs of the various processes, such as semi-monthly pay cycles in payroll, maintenance of human resources documentation, and information systems/cybersecurity controls.
Company A
Company B was primarily concerned with fraud prevention/detection, so GRF leveraged computer-based auditing techniques to identify transactions at high-risk of fraud and analyze large sets of data for potential red flags.
Company B
Cost Savings
Many of the technologies used were the same between both client engagements and both audits were performed within roughly the same budget. GRF was able to address the specific concerns emphasized by management during the planning phase and incorporate additional technologies or increase reliance on certain platforms during the audit process. As a result both companies were able to address high-risk areas identified by management within the budget available through clear identification of engagement objectives, taking advantage of technology, and engaging the expertise of outside consultants.
STEP 3: Summarize Findings and Report on Results
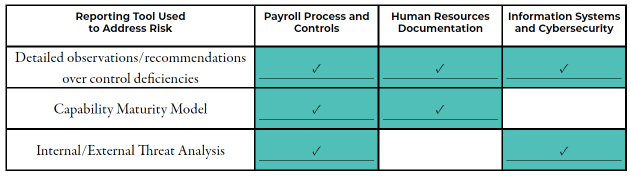
GRF was able to tailor our report and detailed findings to address the risks and objectives identified at the beginning of the assessment. Using the dashboards generated through the audit platforms and our own reporting templates, GRF structured our findings to address each area of risk as follows:
Company A
Company B
Through leveraging a team consisting of CPA, CFE, CEH, CISA, CRISC, and CITP certified professionals, GRF developed reporting tools and templates that were adequately designed to address the identified risks and engagement findings. Both companies were able to take advantage of technologies that would not have been available to them in-house and engaged subject matter experts to carry out the audit procedures to mitigate identified risks to their strategic objectives.
*The organizations featured in this article are clients of GRF CPAs & Advisors, but asked to remain anonymous.
How GRF Can Help
Our clients benefit from the use of these technologies on their engagements through cost savings, enhanced efficiency, and clear results through data visualizations.
If you’re looking to streamline your Internal Audit practice, GRF’s Risk & Advisory Services team consists of subject matter experts across a wide range of fields, which provides a holistic internal audit approach for any organization.
Contact Us
For more information, reach out through our contact us form, or at the info below.